Here’s Your Complete Guide to Hydrostatic Transmission
Share
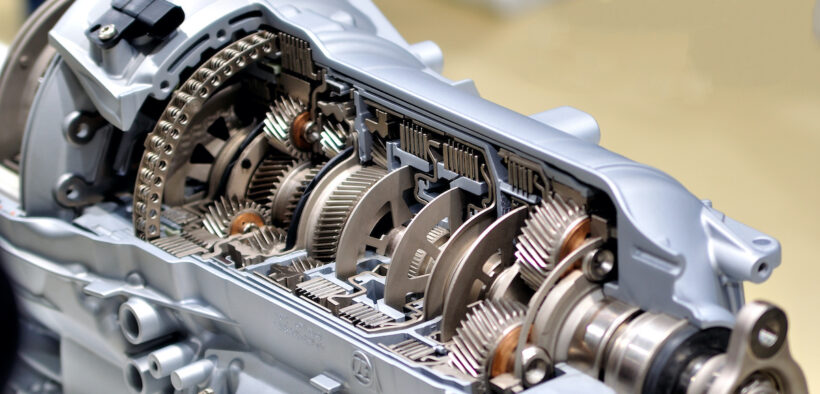
A hydrostatic transmission applies to Page Papi as it does not disrupt engine electricity. Buzzle answers all who question what a hydrostatic transmission is and how it is painted. We explain the blessings and downsides of hydrostatic transmission and several other associated factors.
TAGGED UNDER: Automobile Transmission
Did You Know?
The Honda DN-01 bike was the first purchased street vehicle using hydrostatic transmission.
Most modern-day vehicles use an inner combustion engine. These engines produce rotational motion, but the automobile has to move in a linear style. This is made feasible through the automobile’s transmission, which ‘transmits’ the power generated by using the engine to the automobile’s axle, making the wheels flip. IC engines have the limitation that they can’t function beneath a selected charge, which creates trouble even as stopping or slowing down the vehicle. The transmission also plays this assignment of modifying the engine space by enticing and disengaging gears of various stages. Transmission can be either guided, where the driving force himself has to exchange gears, or computerized, while the vehicle does this undertaking.
Changing gears, either manually or automatically, creates disruptions inside the power transmission of the car. This way, the engine power is reduced momentarily while the gears are being modified. This trouble can be solved using a non-stop variable (CVT), a gearless transmission. The monstrous type of CVT is the hydrostatic transmission, which reveals application not only in heavy equipment, like forklifts, agricultural tractors, and industrial equipment, but also in cars, riding mowers, or even tanks.
READ MORE :
- 10 Tips to Care for Your Skin and Stay Fresh While Traveling
- A 6-Step Guide That Tells You How to Choose a Good CPU Fan
- The competition introduces a component of sport to schoolwork
- 4 Reliable Ways How You Can Recover Deleted Internet History
- A Lucrative, Easy-to-comply with Clothing Line Business Plan
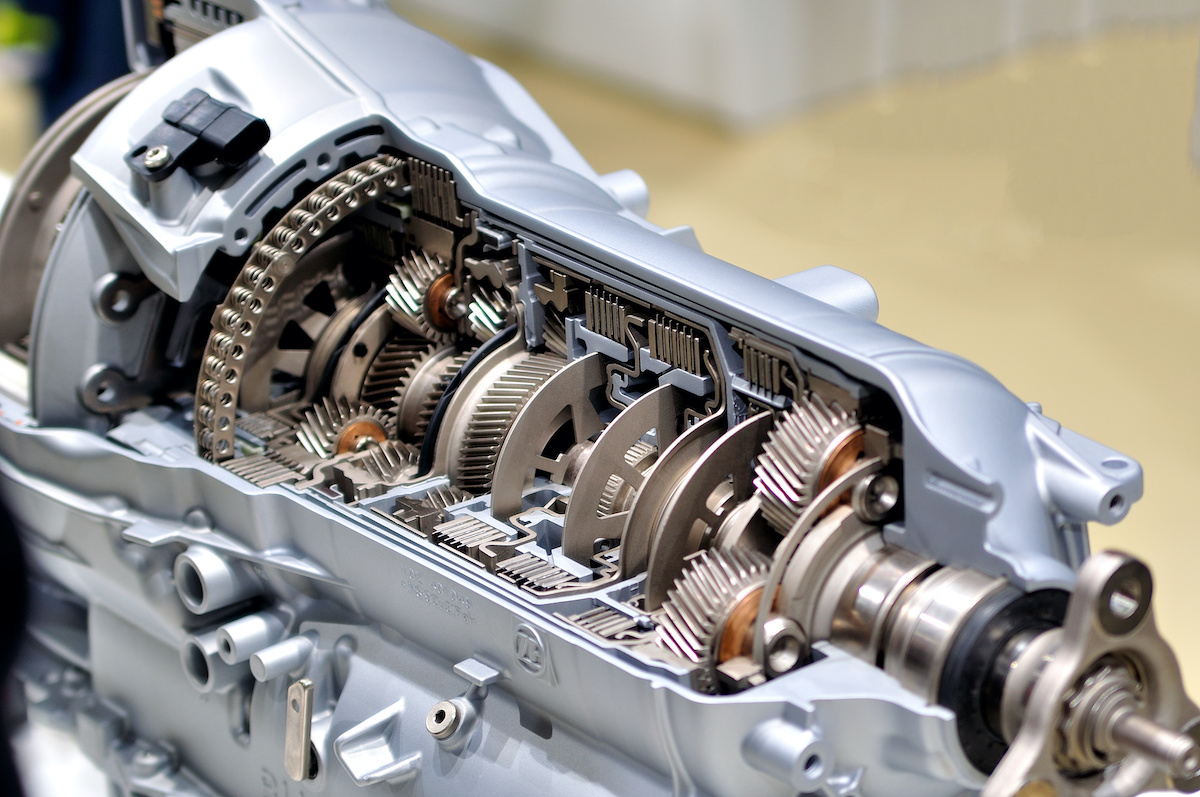
What is Hydrostatic Transmission?
When the power generated by an engine is transferred to the wheels via pressurized fluid instead of with a pressure belt or gears, this kind of transmission gadget is known as a hydrostatic transmission. In this, an IC engine drives a hydraulic pump, which offers pressurized fluid to a motor that is answerable for the motion of the wheels.
How Does Hydrostatic Transmission Work?
A hydrostatic transmission uses the strength of a high mover, such as the crankshaft of an inner combustion engine, to function as a hydrostatic pump motor. The rotary motion from the engine is used to pressurize fluid, which is then directed closer to a hydrostatic drive motor. To accommodate the pressurized fluid, the pistons of the pressure motor must start transferring, therefore developing a rotational movement that turns the wheels. The fluid used is usually oil.
The pressure and quantity of fluid despatched to the pressure motor dictate the rate at which the wheels move. This is managed using a swashplate operated by a hand lever. When the swashplate is vertical, no fluid is despatched to the motor and isn’t operated. When the swashplate is turned around forward using 15º, the car starts transferring inside the forward course. When the swashplate is turned around back when the automobile is in motion, it has a slowing impact. When turned around backward by 7º on a stationary vehicle, its miles are positioned into the reverse transmission by directing the fluid within the backward route.
The hydrostatic transmission is a closed-loop circuit in which the fluid exiting from the power motor outlet is returned to the hydrostatic pump without being sent to the tank. In this circuit, the entering pressure is the hydrostatic pump related to the high mover, and the output power is the force motor associated with the burden.
Types
- Based on Design
- Close-coupled
The hydraulic pump, powerful motor, and other additives are all enclosed in a common housing, with the engine and the pump sharing a not-unusual valve. This enclosed assembly is then bolted to an axle. This kind is compact and economical for packages with area constraints.
In this type, the hydraulic pump and motor are placed in separate locations. However, they are interconnected by excessive-strain hoses or pipes. Because it is more effective, it is used in industrial applications where the desired area is to be reached.
Based on Performance
Fixed-displacement Pump with Fixed-displacement Motor
This typically involves either a variable prime mover or float-manipulate valves, which assist in controlling the velocity. Since the pump has a fixed displacement, it needs to be of an appropriate size to flip the motor. The output torque (turning pressure) or velocity may differ from that of the top mover, depending on the individual displacements of the engine and pump. Reversibility is best if the prime mover can be reversed.
Variable-displacement Pump with Fixed-displacement Motor
This arrangement allows the supply of a constant torque because torque depends totally on motor displacement. Increasing the pump’s potential will grow its rate and strength. It is especially popular as a widespread cause drive, which offers various speeds and ease of manipulation.
Fixed-displacement Pump with Variable-displacement Motor
A fixed-displacement pump helps maintain steady strength, even as the speed and torque may be changed by varying the motor displacement. Lowering the motor displacement increases the velocity, and growing it produces more torque.
Variable-displacement Pump with Variable-displacement Motor
This is the maximum flexible association, which allows for the diffusion of torque and speed-to-energy ratios. While the strength and velocity may be changed by altering the pump displacement, torque depends on the motor displacement. Despite being green and bendy, it has a higher fee.
Advantages
● There is no need to use the snatch and gears, so there is no disruption in transmission.
● A preset-managed speed is feasible in both instructions and impartial from the weight carried.
● There are many quantities of speeds in each, as well as the ahead and reverse guidelines.
● An unmarried lever may be used to manipulate the rate and course.
● Very little maintenance is required besides normal oil and clear-out replacements.
● Hydrostatic transmission can be used to operate electricity steering or dynamic brakes.
● A single top mover may be used to switch strength to diverse locations.
● This transmission has a decreased reaction time when compared to gear transmissions.
● Since it does not now contain an interesting equipment system, power loss because of friction is minimized.
● A kind of torque or electricity to hurry ratios is possible.
● Since the speed and electricity depend on the pressurized fluid, the IC engine can be left working at its most green RPM, substantially lowering gas costs.
Disadvantages
● This system is more costly than the conventional transmission gadget, with the fluid being especially costly.
● The performance of a hydrostatic transmission is slightly decreased, at around 80 – 85%, compared to the ninety-three – ninety-five% of a mechanical transmission.
● The high torque generated can also motivate the problem of wheel spinning on soft surfaces.
● It can’t be towed, like conventional vehicles, which may harm the seals inside the pump by growing back stress. This is because the drive motor turns with the wheels, but the pump does now not.
It’s obvious that the advantages of hydrostatic transmission far outweigh its problems. This is why it is considered an amazing manner of strength transmission, especially when a variable output speed is required.








